George Gilbert Scott was born in Gawcott, Buckinghamshire, England on 13 July 1811 and was articled to James Edmeston (1791-1867) in London from 1827 to 1831. He then worked briefly in the office of Peter & Grissel, a building firm, and for Henry Roberts (1803-1876). He as also an assistant to Sampson Kempthorne (1809-1873) an architect who specialised in the design of workhouses. In 1832 he joined the office of the architect Henry Roberts (1803-1876), who was then working on the Fishmongers' Hall near London Bridge. He left Roberts in c.1835 to set up his own practice and from 1838 was in partnership with William Bonython Moffatt (1812–1887) as Scott and Moffatt. The partnership was dissolved in 1846. Towards the end of his career, he was also in partnership with his second son, John Oldrid Scott (1841-1913) in London.
Read more
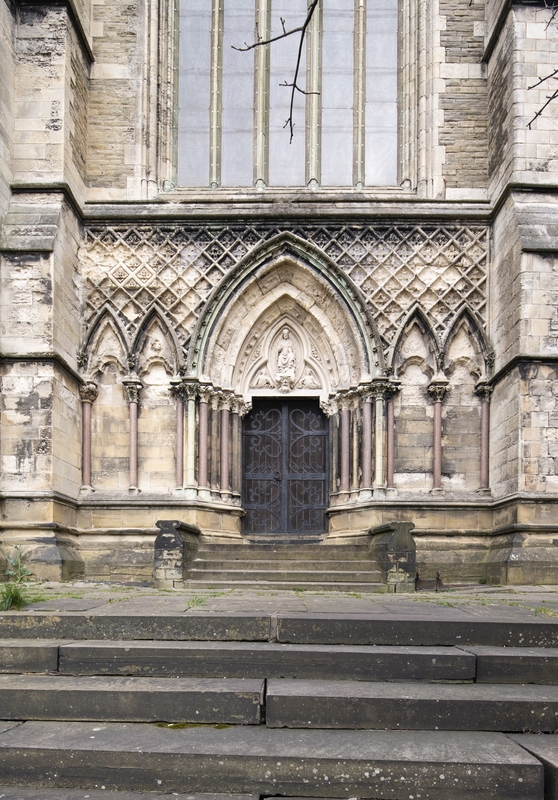
Scott was a prolific architect and was one of the leading exponent of the Gothic Revival. He was known primarily as ecclesiastical architect. Among the many churches, cathedrals and other religious buildings he designed, restored, extended or altered were Vicarage, Wappenham, Northamptonshire (1833); Vicarage, Dinton, Buckinghamshire (1836); Rectory, Weston Turville, Buckinghamshire (1838) Parsonage, Blakesley, Northamptonshire (1839); Parsonage, Hartshill, Stoke on Trent (1840); Parsonage, Hartshill, Stoke on Trent (1840); St Mark's Church, Summerhill, Birmingham (1840-41); Christ Church, Bridlington, Yorkshire (1840–41); St Mary's Church, Hanwell, Middlesex (1841); Holy Trinity, Hulme (1841); St Peter's Church, Norbiton, Surrey (1841); St Giles' Church, Camberwell, London (1841-44); St Mary's Church, Stafford (restored 1842-45); Chantry Chapel of St Mary the Virgin, Wakefield, West Yorkshire (restored 1842); Holy Trinity Church, Hartshill, Stoke on Trent (1842); St John the Baptist's Church, St John's, Woking, Surrey (1842); St John the Baptist Church, Beeston, Nottinghamshire (1842); St Michael and All Angels Church, Wood Green (1843); St Michael and All Angels Church, Wood Green (1843); Church of St Mary and All Saints, Chesterfield, Derbyshire (restoration 1843); St John the Baptist's Church, Leenside, Nottingham (1843–44); Holy Trinity Church, Halstead, Essex (1843–44); St John the Evangelist, West Meon, Hampshire (1843–46); Parsonage, Clifton Hampden, Oxfordshire (1843–46); St Mark's Church, Worsley, Greater Manchester (1844–46); Beverley Minster, Beverley, Yorkshire (additions and alterations, 1844, 1866–68, 1877-80); St Matthias, Malvern Link, Worcestershire (1844–46); St Mary's Church, Nottingham (restoration 1844-72); St Mark's Church, Swindon (1845); Parsonage, Barnet, Hertford (1845); St Matthew’s Church, Donnington Wood, Telford, Shropshire (1845); St Nikolai, Hamburg (1845–80); Parsonage, Wembley, Middlesex (1846); St John the Evangelist, Wembley, Middlesex (1846); The Cathedral of St John the Baptist in St John's, Newfoundland (1847); St Andrew's Parish Church, Spratton, Northamptonshire (1847); St Mary's Church, Sandbach, Cheshire (1847); Ely Cathedral (restoration and alterations 1847–49) ; St Mary the Virgin, Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire (1848); St Gregory's Church, Canterbury (1848); St Paul's Church, Canterbury, Kent (1848); Westminster Abbey (restoration 1848–78); St Cwyfan, Tudweiliog, Gwynedd, Wales (restoration 1849); St Mary's Church, Temple Balsall, Solihull, West Midlands (restoration 1849); St Peter's Church, Northampton (restoration 1849-51); St Peter's Church, South Croydon (1851); St John's Church, Eastnor, Herefordshire Church (1852); St Mary's Church, Halton, Runcorn, Cheshire (restoration 1852); All Saints' Church, Watford, Hertfordshire (1853); St Paul's Episcopal Cathedral, Dundee (1853); Church of St Mary Magdalene, Newark-on-Trent, Nottinghamshire (restoration 1853-55); St Mary's Church, West Derby, Liverpool (1853–6) All Saints' Church, Sherbourne, Warwick (1854); Christ Church, Lee Park, Kent (1854) ; St John the Evangelist, Shirley, Surrey (1854); Holy Trinity Church, Coventry (1854); St Paul's Church, Chippenham (1854–55); Chapel of Exeter College, Oxford (1854–60); Gloucester Cathedral (restoration 1854–76); Holy Trinity Church, Trefnant (1855); St John's Church, Bilton, Harrogate (1855); Coventry Cathedral (restoration 1855–57); Peterborough Cathedral (restoration 1855–60); Lichfield Cathedral (restoration 1855–61, 1877–81); Hereford Cathedral (alteration 1855–63); St Peter, Bushley, Worcestershire (alterations, 1856); Church of St John the Baptist, Glastonbury, Somerset (restoration 1856-57); St Mary, Tedstone Delamere, Herefordshire Chancel (1856–57); Church of St Mary the Less, Cambridge, Cambridgeshire (restoration 1856–57); ; St Mary, Hayes (alterations, 1856-62); All Saints' Church, Oakham, Rutland (restoration, 1857-58); Church of St John the Baptist, Bromsgrove, Worcestershire (restoration 1858); St George's Minster, Doncaster (1858); St George's Minster, Doncaster (1858); St Mary New Church, Stoke Newington (1858); St Matthias Church, Richmond, London (1858); Wakefield Cathedral (restoration 1858–60, 1865–69, 1872–74); All Souls Church, Halifax (1859); St Thomas's Church, Huddersfield (1859); St Matthew's Church, Yiewsley, Hillingdon (1859); St Michael and All Angels Church, Leafield, Oxfordshire (1859–60); St Matthew's Church, Stretton, Cheshire (1859, 1867); Church of St Editha, Tamworth, Staffordshire, with Benjamin Ferrey (restoration, 1850s); St Mary, Edvin Loach, Herefordshire (1860); Great Malvern Priory (1860); Brecon Cathedral (restoration 1860–62 and 1872–75); Bath Abbey, 1860–77; Canterbury Cathedral (restoration 1860, 1877–80); Christ Church, Wanstead, Essex (1861); St Stephen's Church, Higham Green, Suffolk (1861); St John the Evangelist, Sandbach Heath (1861); All Saints' Church, Hawkhurst, Kent (1861); St Mary Magdelene, Duns Tew, Oxfordshire (restoration 1861–62); Chapel of Wellington College, Berkshire (1861–63); St Mary's Church, Hull, East Riding of Yorkshire (restoration 1861–63); Chichester Cathedral (restoration 1861–67, 1872); St John the Baptist Church, Upton Bishop, Herefordshire (restoration 1862); Parsonage, Leith, Midlothian (1862); Vicarage, Jarrom Street, Leicester (1862); All Saints' Church, Langton Green, Kent (1862–63); St Helen's Church, Welton, East Riding of Yorkshire (1862–63); St David's Cathedral, St David’s, Wales (restoration 1862-70); Ripon Cathedral (restoration 1862–72); St Peter and St Paul, Buckingham Church Buckingham (restoration, alteration and additions 1862–78); St Andrew's Hospital Chapel, Northampton (1863); St John the Baptist Church, Aconbury, Herefordshire (restoration 1863); Chapel of St James the Great, Lord Leycester Hospital, Warwick, 1863; St George's Chapel, Windsor Castle, 1863; St John the Evangelist, Taunton (1863); St Edmundsbury Cathedral (restoration 1863–64, 1867–69); Worcester Cathedral (restoration 1863–64, 1868, 1874); St Leonard, Yarpole, Herefordshire, (restoration 1864); St Cuthbert's Church, Darlington (restoration 1864–65); St Clement's Church, Barnsbury (1864–65); Priory Church, Leominster (additions 1864–66, 1876–78); St Andrew's Church, Derby (1864–67); St Andrew's Church, Uxbridge (1865); St John the Baptist, Penshurst (1865); St Luke's Church, Pendleton (1865); St Stephen and St Mark, Lewisham; (1865; St Mary's Church, Shackleford, Surrey (1865); St Mary and St Nicolas, Spalding, Lincolnshire (restoration 1865-67); Salisbury Cathedral (restoration 1865–71); Church of St John the Baptist, Danbury, Essex (1866–67); Holy Trinity Church, Shanghai (1866–69); St Asaph Cathedral (restoration 1866–69, 1871); St Peter's Church, Edensor, Derbyshire (1867–70); All Saints' Church, Winterton, Lincolnshire (1867); St Denys Church, Southampton (1868); St Stephen's Church, Higham Green, Suffolk (1868); St James' Church, Cradley, Herefordshire (addition 1868); Newcastle Cathedral (restoration 1867–71, 1872–76); Chester Cathedral (restoration 1868–75); St Mary's Church, Bishopsbourne, Kent (1871); St Mary Abbots, Kensington, London (restoration 1872); Selby Abbey (restoration 1872–74); All Saints' Church, Hillesden Buckinghamshire (restoration 1874–75); Tewkesbury Abbey (restoration 1874–79); Winchester Cathedral (restoration 1875);St Margaret's Church, King's Lynn (restoration 1875); St Margaret's, Westminster, London (restoration 1877–78); St Mary's Island church on the Orchardleigh Estate, Somerset (restoration 1878); and St Peter's Church, Prestbury, Cheshire (restoration 1879–81)
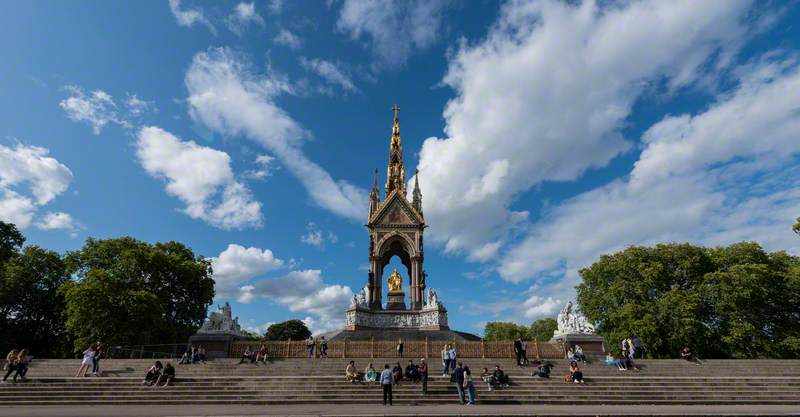
Scott's secular commissions included a large number of workhouses and lunatic asylums; several schools, including Christ Church School, Alsager, Cheshire (1848); and Brighton College, Sussex (1848–66); Reading Gaol in Reading, Berkshire, with William Boynthon Moffatt (1842-44); Leeds General Infirmary (1864-67); Midland Grand Hotel, St. Pancras Station, London (1865-73); Brill Swimming Baths, Brighton, Sussex (1866–69); an extension to Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford (1869–71); building at Bombay University [now Mumbai University] (1869-78); and the Albert Memorial, Kensington Gardens, London (completed 1872).
Scott was the author of numerous books, pamphlets, articles and reports on architecture. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Institute of British Architects (FRIBA) in 1849); an Associate of the Royal Academy (ARA) in 1855; a Royal Academician (RA) in 1860; and a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries (FSA) in 1860. He was awarded the RIBA Royal Gold Medal in 1859 and knighted for his services to architecture in 1872.
He died at 39 Courtfield Gardens, South Kensington, London on 27 March 1878.
Text source: Art History Research net (AHR net)